





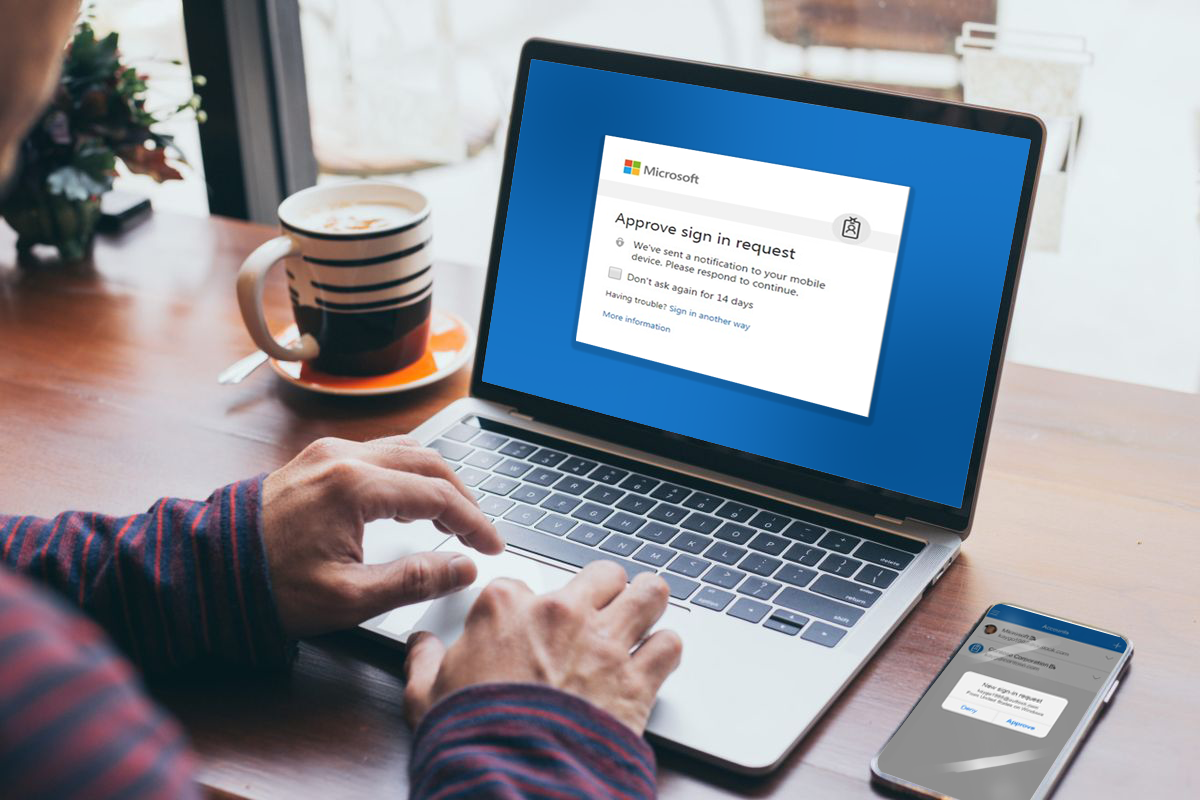
When you sign into your online accounts, you're proving to the service that you are who you say you are. This process is known as "authentication" and has traditionally been done with a username and password.
Usernames are easy to discover; sometimes they're just your email address. Passwords can be hard to remember, so people tend to pick simple ones, or use the same password for many accounts.
If you’re one of the 54% of consumers who, according to TeleSign, use five or fewer passwords for all of their accounts, you could create a "domino effect" that allows hackers to take down multiple accounts just by cracking one password.
There’s an easy way to better protect your accounts: multi-factor authentication (otherwise known as MFA).
MFA is an authentication method that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to online resources. Rather than just asking for a username and password, MFA requires additional verification factors, which decreases the likelihood of a successful cyber-attack.
For this reason, it has become a universal requirement for cybersecurity insurance providers. This means a few things, but the most important one to you is the following:
If your company has Cybersecurity or Technological Insurance, you will see rate hikes or complete policy cancellation without active MFA measures in place.

MFA methodology is based on requesting one of three types of additional information from the user, on top of their standard password:
· Things you know (knowledge).
· Things you have (possession).
· Things you are (inherence).
Let's say you're going to sign into your bank account, and you enter your username and password. If that's all you need then anybody who knows your username and password can sign in as you!
If you have multifactor authentication enabled, there are more steps to access your account. When you sign in you enter your username and password, then you get prompted to enter a second factor to verify your identity.
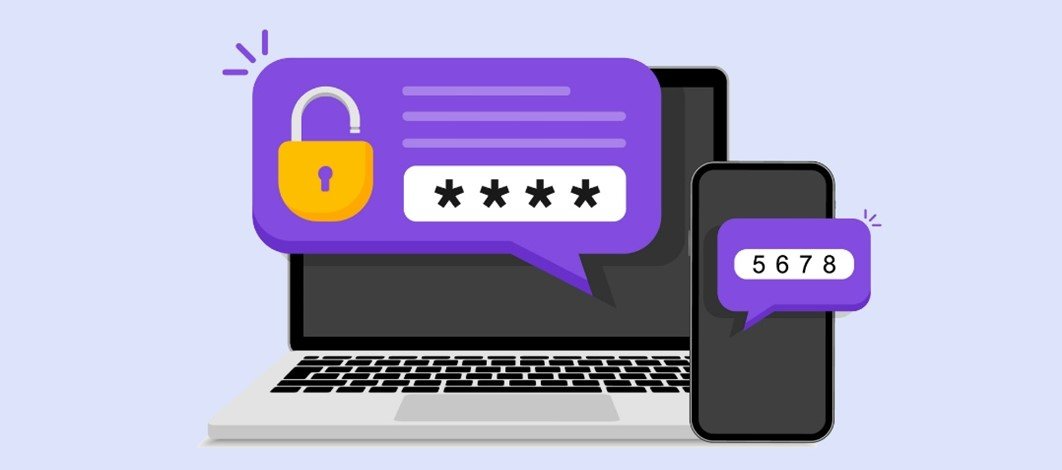
One of the most common MFA methods used is one-time passwords (OTP). OTPs are 4-8 digit codes that you receive via email, SMS or via a smartphone authentication app. With OTPs, a new code is generated periodically or each time an authentication request is submitted.
Here are Some Other Common Examples:
KNOWLEDGE
POSSESSION
INHERENCE

Using MFA is one of the top three things that security experts do to protect their security online. Consumers feel the same way: almost 9 in 10 (86%) say that using MFA makes them feel like their online information is more secure, according to TeleSign.
Compromised passwords are one of the most common ways that bad guys can get at your data, your identity, or your money. Using multifactor authentication is one of the easiest ways to make it a lot harder for them.
Contact the IT Professionals at Seifert Technologies to learn more about Multi-Factor Authentication and securing your accounts.









All Rights Reserved | Seifert Companies