Machine Learning (AI) Trends Are Changing Manufacturing
The Industrial Internet of Things has and continues to help manufacturers. IIoT has made manufacturing efficiency, safety, and productivity better than ever before. Now the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning has joined the party. AI and machine learning simplifies managed data collected during manufacturing.
Machine Learning and AI
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
“Artificial Intelligence is the field of developing computers and robots that are capable of behaving in ways that both mimic and go beyond human capabilities.” AI-enabled systems can analyze and contextualize data. The data collected provides information and triggers actions without human interference. AI in manufacturing fields uses technology to automate complex tasks. It also seeks out and finds unknown patterns in manufacturing processes and workflows. AI in manufacturing uses data to make faster, more accurate decisions. AI systems are quicker and more reliable than human operations.

What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning and artificial intelligence are often thought to be the same. People use both when referring to the same concept, but they're actually different. AI is a broad concept of using machines or computers to replicate human thinking. Machine learning is more specific, it's an application of AI. Machines and computers are able to learn without the need for human programming. “Machine learning is a pathway to artificial intelligence. This subcategory of AI uses algorithms to automatically learn insights and recognize patterns from data, applying that learning to make increasingly better decisions.” It works by big amounts of data to train algorithms. These algorithms are then used on new data to find hidden patterns and predict outcomes. Machine learning allows algorithms to learn and improve processes on their own. This makes them like humans, only without the need for humans. There are two different types of machine learning. These include supervised and unsupervised machine learning.
Types of ML in Manufacturing
Supervised Machine Learning
Supervised machine learning is an approach that’s defined by its use of labeled datasets. These datasets can train or administer algorithms into classifying data or predicting outcomes. Using labeled inputs and outputs, the model can measure its accuracy and learn over time. Two types of problems are possible when supervised data mining occurs. These include:
- Classification: These problems use an algorithm to assign test data into specific categories. There are common types of classification algorithms. These include linear classifiers, support vector machines, decision trees and random forests.
- Regression: Using an algorithm to understand the relationship between dependent and independent variables. Regression models are helpful for predicting numerical values based on different data points. Some popular regression algorithms are linear regression, logistic regression, and polynomial regression.
Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised machine learning uses algorithms to analyze and cluster unlabeled data sets. These algorithms discover hidden patterns in data without the need for human intervention. This is why they're labeled as unsupervised. Unsupervised learning models are beneficial for three main tasks:
- Clustering: This is a data mining technique for grouping unlabeled data. based on their similarities or differences. This technique is helpful for market segmentation, image compression, etc.
- Association: Uses different rules to find relationships between variables in a given dataset. These methods are beneficial for market basket analysis and recommendation engines. For example, “Customers Who Bought This Item Also Bought” recommendations.
- Dimensionality Reduction: When features or dimensions in a given dataset is too high. This reduces the number of data inputs to a manageable size. It does this while also preserving the data integrity. Often, this technique is best in the preprocessing data stage.

Uses of ML in Manufacturing
- Predictive Maintenance: Tech draws from machine and equipment data to identify patterns. These patterns point to possible failure. This lets relevant operators and maintenance crews fix machines before they break down. This reduces downtime so that the line continues moving.
- Supply Chain Management: Manufacturers rely on their suppliers providing high-quality materials. High quality materials are beneficial for the production process. AI and machine learning can sort through different supply-chain-related tasks. These include warehouse and inventory management, inbound and outbound shipments, and customer demand. This prevents manufacturers from falling behind on order fulfillment and productivity.
- Utilizing Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical objects. In manufacturing, this relates to new products, equipment and even shop floor layouts. Manufacturing businesses leverage machine learning to optimize product design. They also use it to customize the production line. These things create more efficient operation.
- Utilizing Energy and Prediction: Machine learning analyzes raw data from factory machines. This creates patterns that showcase energy consumption and preventing it. Additionally, manufacturers use the technology to predict future consumption, allowing proper planning.
- Predictive Quality and Yield: Machine learning detects causes of yield losses. It also detects causes of quality defects. The tech identifies probable wastage causes, allowing manufacturers to adjust their operations.
Machine Learning with Keyence
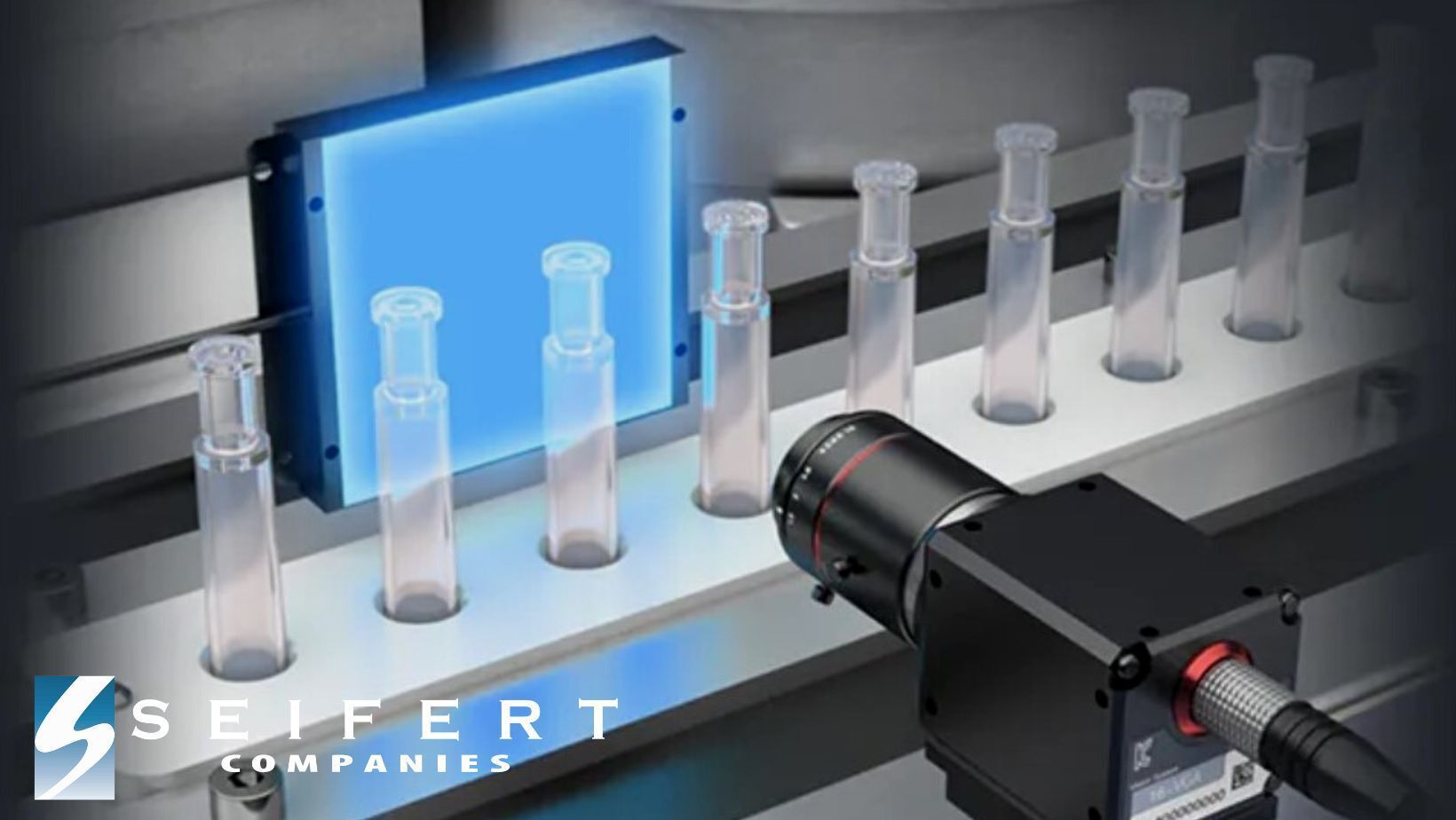
"A vision system combines industrial cameras, lenses, and lighting to automate visual inspections of manufactured products." Here at Seifert, Keyence is a brand of vision system we use. Keyence offers the most complete vision system lineup. The CV-X Series is an innovative easy to use system. It uses high-speed cameras to solve inspection applications across all manufacturing industries. It incorporates cameras and lighting to photograph parts in-line. This process improves efficiency and ensures quality. This system can be beneficial to automotive, electronic, medical, food and packaging manufacturing. You can learn more about their products through their online catalogs. Common applications include:
- Defect detection
- Surface inspection
- Presence of parts and features
- Assembly verification
- Vision guided robotics
- Measurement
- Code reading
According to Full Scale, Machine learning and vision systems relate to one another. Machine learning has improved computer vision about recognition and tracking. It offers effective methods for acquisition, image processing, and object focus. Vision systems broaden machine learning. They involve images/videos sensing devices, interpreting devices, and the interpretation stage. Machine learning is useful in both the interpreting device and interpretation stage.
Conclusion
AI and machine learning is gaining popularity in the manufacturing world. These processes simplify data collection and workloads. Increased availability of data and computing power justify this claim. Adopting AI and machine learning processes will lead to optimized machine usage. Investing in a vision system could go hand in hand with machine learning and AI. If you’re thinking about adapting any of these things into your business, get in touch. Let's assess your manufacturing processes and determine what’s best for you. Contact us today to learn more!